- Time:2023-01-04
- View:656
- Font:

- Author:admin
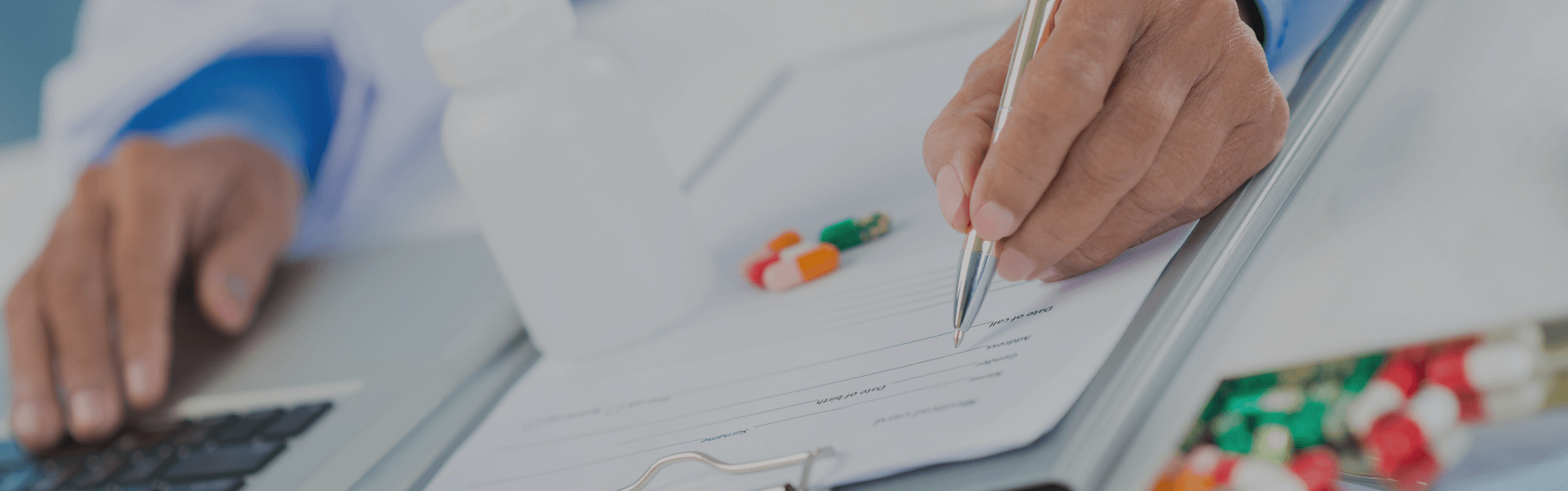
1. Endoscopic insertion: Patients generally take the prone or left lateral position, and the duodenoscope enters the descending segment of duodenum through the esophagus, stomach, and then finds the duodenal papilla.
2. Intubation: Selective intubation is the basis for successful diagnosis and treatment of ERCP. Insert the catheter through the biopsy hole, adjust the Angle button and the forceps lifter to make the catheter perpendicular to the nipple opening, and insert the catheter into the nipple. The success rate of intubation by most ERCP physicians should be more than 85%, and the success rate of selective intubation guided by the guide wire is high, with fewer complications.
3. Angiography: The contrast agent was injected through the angiographic catheter under fluoroscopy, and bile duct or pancreatic duct development was seen on the fluorescent screen, showing the lesions. Minimize unnecessary pancreatic duct development to prevent postoperative pancreatitis.
4. Radiography: After pancreatobiliary duct development, radiography was performed for storage.
5. Treatment: Different endoscopic treatment measures (such as sphincterotomy and lithotomy, placement of drainage tube or stent to relieve bile duct obstruction, placement of fistula stent, etc.) were taken according to the patients' conditions of pancreatic bile duct lesions.